为什么要用到函数式组件?
react官网:
class难以理解:
- Javascript的this指针
- 官方进行组件预编译优化,class常常让优化措施无效
理解React?
- React框架? 不同于angular,react官网并不称自己为框架:用于构建用户界面的JavaScript库
路由,状态管理,并不是react团队开发的,而是交给社区做,所以它并不完全能叫一个框架,只是一个库。
- react使用者上限和下限差距极大,会使用很简单,成为高手比较难
React优势
组件化,高内聚低耦合,但并没有提供一整套解决方案,需要依靠社区提供的集成方案
JSX代码可读性好
为什么React选择JSX?其他方案为什么不好
JSX本质
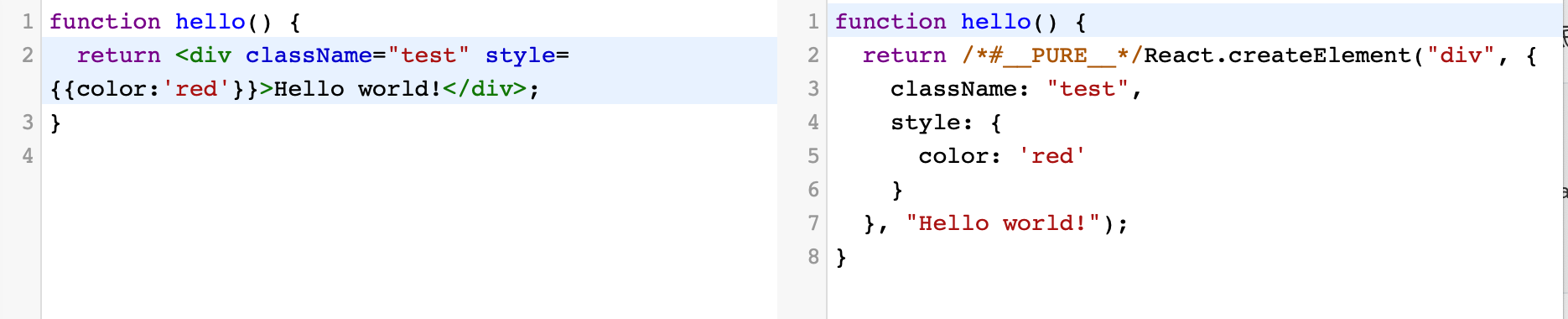
官网:实际上,JSX 仅仅只是 React.createElement(component, props, ...children) 函数的语法糖。
<MyButton color="blue" shadowSize={2}>
Click Me
</MyButton>
被编译为:
React.createElement(
MyButton,
{color: 'blue', shadowSize: 2},
'Click Me'
)
接着会产生疑问:React.createElement()到底是一个什么样的方法?
React.createElement(
type, //第一个参数为html标签名称
[props], //第二个参数为属性,如className
[...children] //第三个参数为子结点
)
在react文件中,第一句常常是:
import React from 'react';
但是程序中却没有出现显式的对引入的React的调用,删了这一句也不行
查:
在渲染Dom的时候调了React.createElement()
在https://babeljs.io中可以看到该过程:
看createElement()源码:
/**
* Create and return a new ReactElement of the given type.
* See https://reactjs.org/docs/react-api.html#createelement
* type: 节点类型
* 如果是原生的节点类型,那么就是一个字符串 tagName
* 如果是一个组件(我们自己定义的、或者React内置提供的)那么就是一个变量
*
* config: 就是写在jsx上的属性,它们都会转为key: value格式存到config对象上
*
* children: 所有后代元素
*/
export function createElement(type, config, children) {
let propName;
// Reserved names are extracted
// 对于组件内部来说传入的属性就是props
const props = {};
// 预定义key ref等变量用于后面存值
// key ref属于特殊的attrs需要剔除
let key = null;
let ref = null;
let self = null;
let source = null;
if (config != null) {
if (hasValidRef(config)) {
// 存储合法的ref
ref = config.ref;
}
if (hasValidKey(config)) {
// 存储合法的key => string
key = '' + config.key;
}
self = config.__self === undefined ? null : config.__self;
source = config.__source === undefined ? null : config.__source;
// 其他属性枚举到props对象
for (propName in config) {
if (
// 仅限config自身的属性 && 排除React预留的props
hasOwnProperty.call(config, propName) &&
!RESERVED_PROPS.hasOwnProperty(propName)
) {
props[propName] = config[propName];
}
}
}
// Children can be more than one argument, and those are transferred onto
// the newly allocated props object.
// 获取children的个数,一个节点下的children是可以有多个的
const childrenLength = arguments.length - 2;
// 赋值处理props.children
if (childrenLength === 1) {
props.children = children;
} else if (childrenLength > 1) {
// 定长数组、再遍历拷贝
const childArray = Array(childrenLength);
for (let i = 0; i < childrenLength; i++) {
childArray[i] = arguments[i + 2];
}
if (__DEV__) {
if (Object.freeze) {
Object.freeze(childArray);
}
}
props.children = childArray;
}
// Resolve default props
// 处理defaultProps,另外需要处理defaultProps的顺序
/**
* class CustomButton extends React.component{}
* CustomButton.defaultProps = {}
* 可见type是一个组件
*/
if (type && type.defaultProps) {
const defaultProps = type.defaultProps;
for (propName in defaultProps) {
// 如果 props.color 被设置为 null,则它将保持为 null
// 关于这里为什么是undefined、而不是null,其实很好理解,定义了一个遍历而不初始化那它就是undefined,而null需要手动初始化。
if (props[propName] === undefined) {
props[propName] = defaultProps[propName];
}
}
}
if (__DEV__) {
if (key || ref) {
// 处理displayName,即推导过程
// 如果是组件、先从组件的displayName取、其次是组件的名字、最后是默认值
const displayName =
typeof type === 'function'
? type.displayName || type.name || 'Unknown'
: type;
if (key) {
defineKeyPropWarningGetter(props, displayName);
}
if (ref) {
defineRefPropWarningGetter(props, displayName);
}
}
}
// 返回一个真正的ReactElement
return ReactElement(
type,
key,
ref,
self,
source,
ReactCurrentOwner.current,
props,
);
}
/**
* Factory method to create a new React element. This no longer adheres to
* the class pattern, so do not use new to call it. Also, no instanceof check
* will work. Instead test $$typeof field against Symbol.for('react.element') to check
* if something is a React Element.
*
* @param {*} type
* @param {*} props
* @param {*} key
* @param {string|object} ref
* @param {*} owner
* @param {*} self A *temporary* helper to detect places where `this` is
* different from the `owner` when React.createElement is called, so that we
* can warn. We want to get rid of owner and replace string `ref`s with arrow
* functions, and as long as `this` and owner are the same, there will be no
* change in behavior.
* @param {*} source An annotation object (added by a transpiler or otherwise)
* indicating filename, line number, and/or other information.
* @internal
*/
const ReactElement = function(type, key, ref, self, source, owner, props) {
const element = {
// This tag allows us to uniquely identify this as a React Element
// 通过Symbol作为独一无二标识符 Symbol.for进行复用
$$typeof: REACT_ELEMENT_TYPE,
// Built-in properties that belong on the element
// 节点类型
type: type,
key: key,
ref: ref,
props: props,
// Record the component responsible for creating this element.
_owner: owner,
};
if (__DEV__) {
// The validation flag is currently mutative. We put it on
// an external backing store so that we can freeze the whole object.
// This can be replaced with a WeakMap once they are implemented in
// commonly used development environments.
element._store = {};
// To make comparing ReactElements easier for testing purposes, we make
// the validation flag non-enumerable (where possible, which should
// include every environment we run tests in), so the test framework
// ignores it.
Object.defineProperty(element._store, 'validated', {
configurable: false,
enumerable: false,
writable: true,
value: false,
});
// self and source are DEV only properties.
Object.defineProperty(element, '_self', {
configurable: false,
enumerable: false,
writable: false,
value: self,
});
// Two elements created in two different places should be considered
// equal for testing purposes and therefore we hide it from enumeration.
Object.defineProperty(element, '_source', {
configurable: false,
enumerable: false,
writable: false,
value: source,
});
if (Object.freeze) {
Object.freeze(element.props);
Object.freeze(element);
}
}
return element;
};
为什么选择JSX**?**
JSX 语法糖允许前端开发者使用我们最为熟悉的类 HTML 标签语法来创建虚拟 DOM,在降低学习成本的同时,也提升了研发效率与研发体验
React高性能体现:虚拟DOM
(参考资料:https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV19p4y1z7LK?p=9&spm_id_from=pageDriver)
Web开发需要将变化的数据实时反映到UI上,需要我们频繁地操作DOM,这就是性能瓶颈的原因(如何进行高性能的复杂DOM操作?)
React:引入Virtual DOM。在浏览器端用Javascript实现了一套DOM API。基于react开发的所有DOM构造都通过虚拟DOM进行。
当数据变化 ,react重构DOM树,将当前树和上一次树进行对比,得到DOM的区别,仅仅更新变化的部分。
**(精髓)**存在一个Event loop,在一个loop中两次数据变化会被合并,A->B->A在一个loop中发生,UI不发生任何变化。react认为不变,所以不会更新到B,再更新到A。
频繁更新虚拟DOM,性能不会差?
虚拟DOM是内存数据,性能高,对实际DOM进行操作的仅仅是Diff部分。
React Fiber
不是上面的Event Loop。
是React 16之后发布的一种核心算法。官网:是对核心算法的重新实现。之前用的是diff算法。
为了解决的问题:之前的react,更新过程是同步的,可能导致性能问题。
React决定加载或更新组件时,会干很多事,比如:调用各个组件生命周期,计算比较虚拟DOM树,更新DOM树。这个过程是同步进行的,一次加载/更新开始,中间不会中断。因为JS是单线程,组件树很大时,每个同步任务耗时太长,出现加载卡顿。
React Fiber:分片。把耗时的任务分成若干片。每一片运行时间很短。每一小片执行完成之后,都会给其他任务机会去执行,从而避免进程被独占。(很像CPU的时间片,把cpu资源类比于js单线程,把线程类比于react中的很多任务)

生命周期
16.3之前
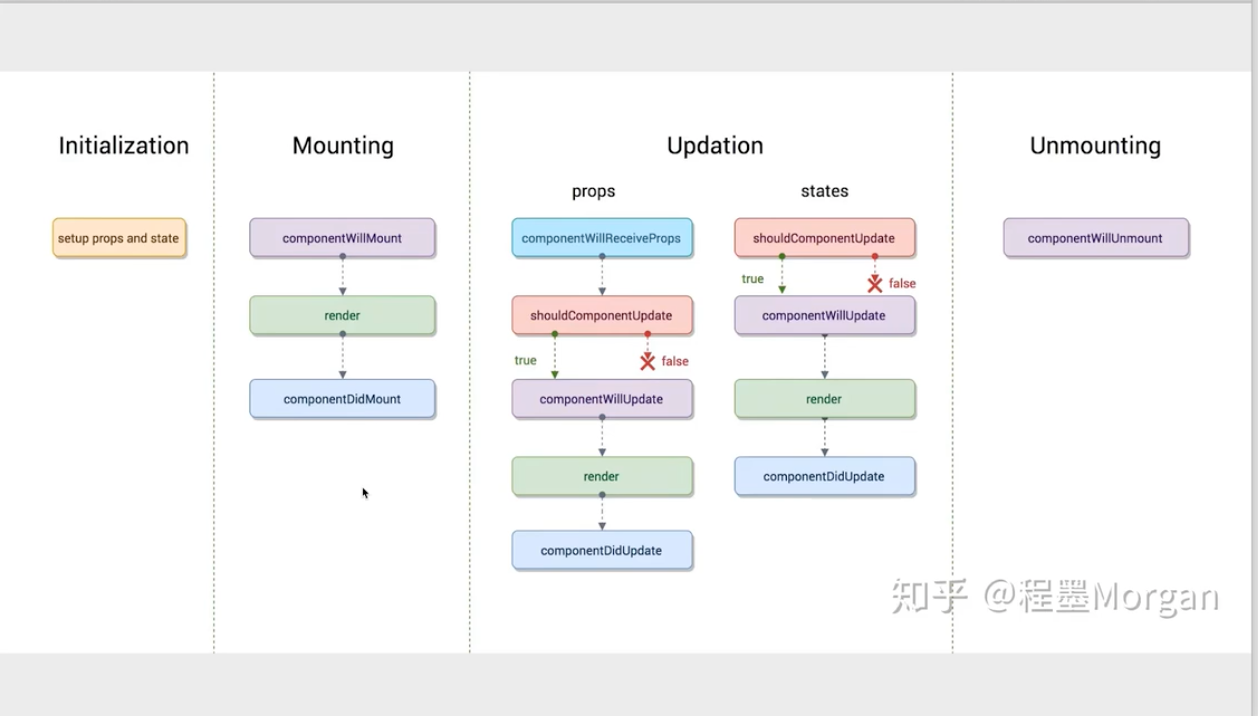
现在的生命周期:
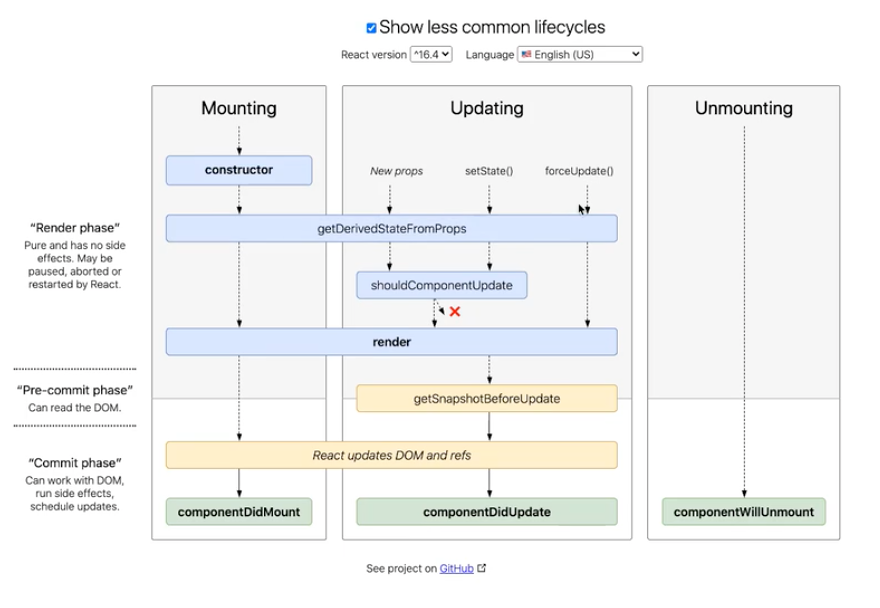
getDrivedStateFromProps(): 根据props生成state
官网不推荐使用,容易写出bug
Redux
Flux: Redux鼻祖
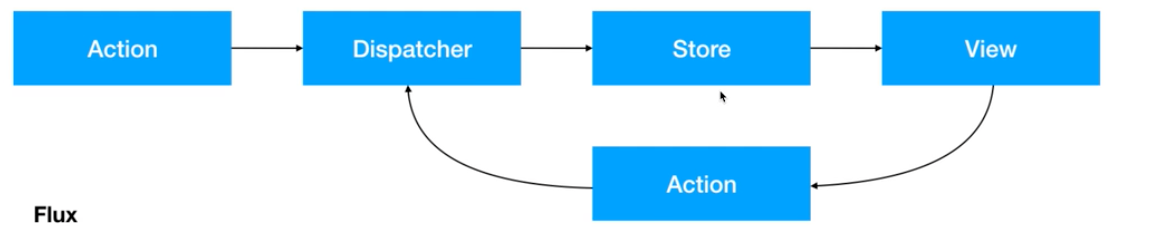
- View:视图层
- ActionCreator :视图层发出的消息
- Dispatcher: 用来接受Action,执行回调函数
- Store(数据层):用来存放应用的状态,一旦发生变动,提醒Views更新界面
但是Flux实现太复杂
需要Redux的项目
- 用户使用的方式复杂
- 不同身份用户有不同的使用方式
- 多个用户之间可以协作
- 与服务端大量交互,或者使用了websocket
- View需要从多个来源获取数据
从组件层面考虑:
- 某个组件的状态需要共享
- 某个状态在任何地方都可拿到
- 一个组件需要改变全局状态
- 一个组件需要改变另一个组件的状态
设计思想:
1、Web应用是一个状态机,数据和视图一一对应
2、全局状态保存在一个对象中